<!DOCTYPE html>
Understanding Acute Shoulder SynovitisWhat is Acute Shoulder Synovitis?
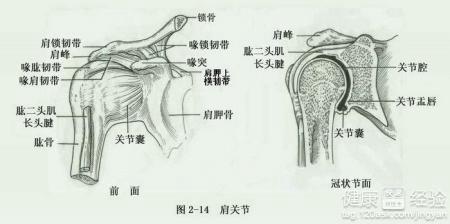
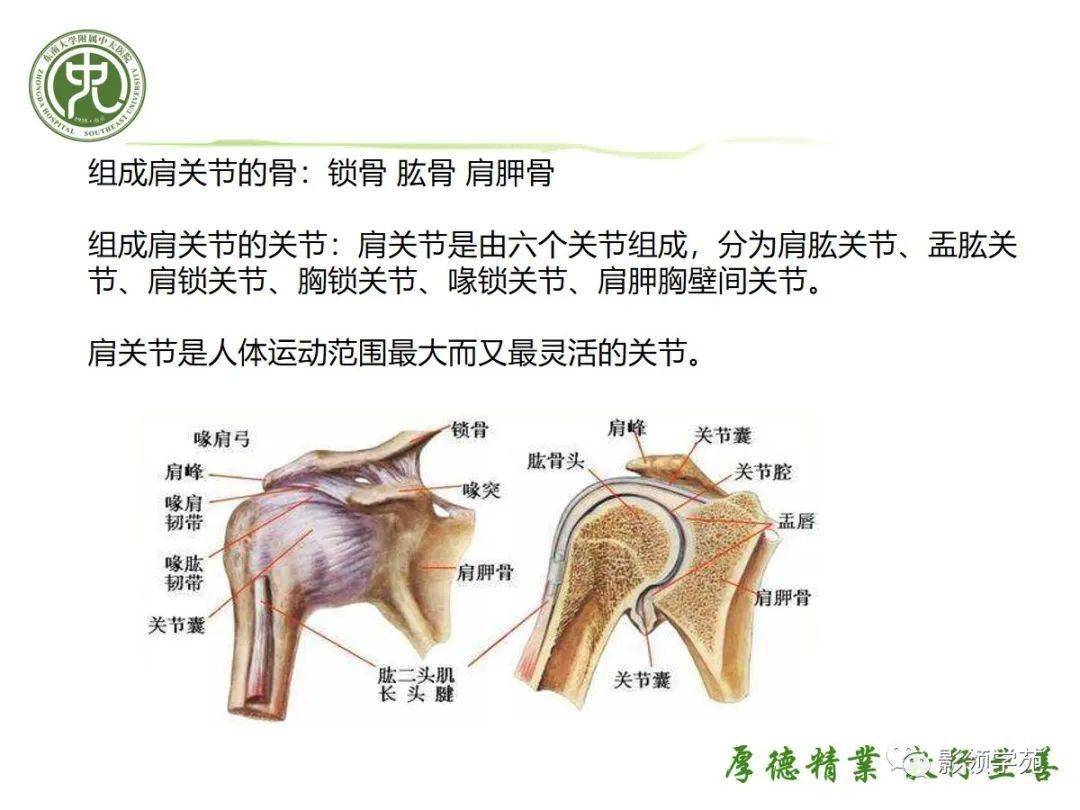
Acute shoulder synovitis refers to the inflammation of the synovial membrane, which is the lining of the shoulder joint. This condition is often sudden and can cause significant pain and discomfort. The synovial membrane produces synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint and reduces friction during movement. When this membrane becomes inflamed, it can lead to a range of symptoms that affect the shoulder's functionality.
Causes of Acute Shoulder Synovitis
The primary cause of acute shoulder synovitis is inflammation, which can be triggered by various factors. Some common causes include:
- Infection: Bacterial or viral infections can lead to the inflammation of the synovial membrane.
- Injury: Trauma or an injury to the shoulder joint can cause the synovial membrane to become inflamed.
- Overuse: Repetitive stress or overuse of the shoulder joint can strain the synovial membrane.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis can cause the body's immune system to attack the synovial membrane.
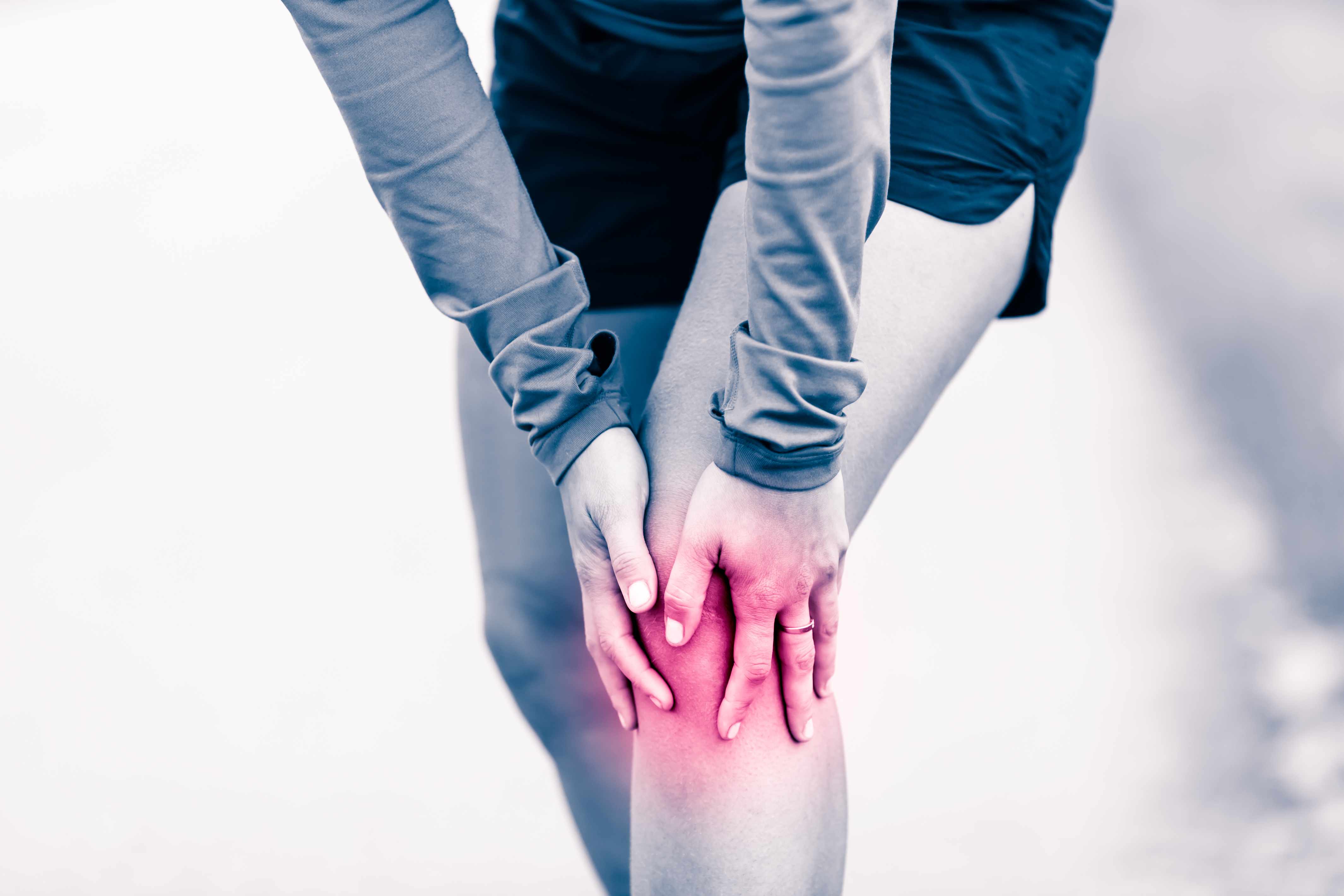
Symptoms of Acute Shoulder Synovitis
The symptoms of acute shoulder synovitis can vary depending on the underlying cause and the extent of the inflammation. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: The shoulder may be painful, especially with movement.
- Swelling: The joint may appear swollen and feel tender to the touch.
- Reduced range of motion: The shoulder may be stiff, and the range of motion may be limited.
- Redness: The shoulder area may appear red or pink.
- Heat: The joint may feel warm to the touch.
Diagnosis of Acute Shoulder Synovitis
A healthcare professional will typically diagnose acute shoulder synovitis based on a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests. These may include:
- Physical examination: The healthcare provider will assess the shoulder's range of motion and check for signs of swelling and tenderness.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound may be used to visualize the shoulder joint and detect any structural abnormalities.
- Lab tests: Blood tests can help identify infection or autoimmune diseases that may be contributing to the inflammation.
Treatment Options
Treatment for acute shoulder synovitis aims to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and restore joint function. Common treatment options include:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms can help reduce inflammation.








 蜀ICP备2022005971号-1
蜀ICP备2022005971号-1
还没有评论,来说两句吧...